Humans and Climate Change
The Carbon Cycle
The sun constantly supplies energy to food chains, it is always entering and leaving ecosystems.
But the supply of nutrients to living organisms is limited and these elements must be recycled.
Nutrients are recycled between the abiotic (non living) and biotic (living) parts of ecosystems.
One element that all living things require is carbon:
- It provides a source of energy when it is used in respiration
- It is needed for cell growth
Since there is only a certain amount of carbon on earth, it is constantly being recycled through ecosystems.
The Carbon Cycle
Basic Definition: it is a series of processes by which carbon compounds are inter-connverted in the environment.
Processes:
Carbon enters the atmosphere as carbon dioxide from respiration and combustion.
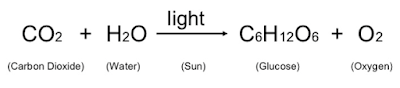
Carbon dioxide gets absorbed by producers (plants) to make carbohydrates during photosynthesis.
Animals feed on the producers (plants) passing the carbon compounds along the food chain. Most of the carbon they consume is exhaled as carbon dioxide formed during respiration. The rest of the carbon goes toward making proteins (e.g. carbohydrates) for the animals.
The animals and plants eventually die.
The dead animals and plants are decomposed by decomposers and the carbon left in their body is returned to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
In some conditions decomposition cannot occur as conditions (e.g. temperature or oxygen availability) are not suitable for decomposers to survive, the remain of the dead plant and animals if subjected to high pressure and heat for million of years they become fossil fuels.
- This traps carbon in them and cannot be released back into the atmosphere
However, humans now exploit fossil fuels as a source of energy through combustion of fossil fuels which release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere.
Burning of other fuels like wood and alcohol also release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere
Additional processes that may be useful to know:
- In the sea, some animals (e.g. hermit crabs, sea molluscs) turn carbon into calcium carbonate which is used to make their bones and shells.
- When they die their bones and shells fall to the ocean floor and eventually become limestone and chalk
- Volcanic eruptions release carbon dioxide
- A lot of carbon dioxide is absorbed and dissolved in the oceans and other bodies of water
Diagram illustrating the carbon cycle:
Carbon Dioxide Atmospherical Concentrations
Combustion of fossil fuels
The combustion of fossil fuels increases carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere.
Used for:
- Heating our homes
- Electricity
- Powering facilities
- Powering cars, airplanes
- etc
When fossil fuels are burnt they release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Fossil fuels have trapped carbon inside them because it never was released as it was not decomposed.
When you burn fossil fuels, they release their trapped carbon into the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide.
Deforestation
It occurs for:
- Land clearing (for agriculture, expansion of cities, mining, etc)
- Biomass (fuelwood for e.g. fireplace)
- Logging - for paper products
Method of deforestation used are:
- Felling (cutting down trees)
- Slash and burn technique
How does deforestation increase carbon dioxide concentrations?
Plants take in CO2 and give out O2. Plants are a way of removing CO2 from the atmosphere and if these plants of removed there is nothing removing the carbon dioxide from the air and therefore this increases CO2 atmospherical concentrations.
Plants are a major carbon store (they store carbon). When the trees are cut/ burnt they release all the stored carbon back into the atmosphere in the form of CO2. Therefore increasing carbon dioxide atmospherical concentrations.
Undesirable effects of Deforestation
Extinction of plant and animal species
- loss of habitat
- killed in the slash and burn method
Loss of soil/ erosion
- Vegetations holds and grounds the soil protecting it from heavy rainfall. When there is no vegetation, the soil becomes lose and vulnerable to heavy rainfall.
- Heavy rainfall washes away soil therefore leading to erosion
Flooding
- With trees:
- prevents sediment runoff
- rainwater caught by leaves reduces impact on soil, therefore less soil erosion
- tree roots absorb the water from the soil
- Without trees:
- nothing to reduce the impact of rainfall on soil therefore leading to soil erosion
- nothing to absorb the water from the soil
Therefore results in build ups of water therefore leading to floods.
Increased carbon dioxide atmospherical concentrations
Greenhouse Gas Effect
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface.
When the sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and re-radiated by a layer of greenhouse gases surrounding the earth's atmosphere.
The absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and the surface of the Earth.
This process maintains the Earth's average temperature at around 15 degrees celsius, therefore allowing life on Earth to exist.
Examples of greenhouse gases (GHG):
- Water vapour - main greenhouse gas (58%)
- Carbon dioxide
- Methane
- Nitrous oxide
- Ozone
- Artificial chemicals (e.g. chlorofluorocarbons (CFC's))
This phenomena naturally occurs. However due to human activities such as: combustion of fossil fuels, deforestation and agriculture are increasing the concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
A thicker layer of GHG's means less heat energy escapes back to space and more is radiated back to earth.
Diagram illustrating how the greenhouse gas effect works
Effects of the enhanced greenhouse gas effect:
- Climate change
- higher frequency of extreme weather events occurring
- E.g. droughts, tropical storms
- Rising sea levels due to the melting polar ice caps due to the increasing temperature
- Increasing pH level in oceans (becoming more acidic)
- Plants and animals will no longer be able to survive in their currently changing habitats and may become extinct
- Diseases that were once restricted to warm, tropical areas will be able to spread all over the world as the Earth gets hotter
- Crop failure due to changing and extreme weather and climate
Fossil Fuels
Most energy we use today comes from fossil fuels.
There are three main types of fossil fuels that we use:
They are used as fuels because they give out a lot of heat when they are burned (extremely exothermic reaction).
Combustion
Fuels store chemical energy and when we burn them this energy is released and produces heat and/or light.
When fuels are burned this is called a combustion reaction.
Three thing are required to burn a fuel:
- Fuel
- Heat
- Oxygen
When hydrocarbons (like fossil fuels) burn they are oxidised.
They react with oxygen gas from the air and give off heat as well as produce carbon dioxide and water.
General formula:
Hydrocarbon + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water
Fossil fuels are burned in power plants to generate electricity and also in cars and planes.
Fossil Fuel Power Plants
In power plants, the fuels are burned and high amounts of heat they produce are used to heat water until it boils and becomes steam.
This steam then turns a generator, which produces electricity that can be sent out to surrounding communities.
Problems
The problem with burning fossil fuels is that it releases carbon that has been stored in them for million of years is released into the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide.
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, meaning it remains in the atmosphere and traps thermal radiation (heat) close to the Earth's surface.
Radiation from the sun is allowed to enter but it cannot escape.
This causes the temperature of the earth to increase, known as global warming.
Some fossil fuels also contain sulphur which burns in the air to form sulphur dioxide, which causes acid rain.
Fossil fuels are non-renewable meaning they will run out in time.
Alternatives to Fossil Fuels
Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy is non-renewable however only a very small amount of nuclear fuel is required to release a huge amount of energy.
The most common nuclear fuel used in nuclear power stations is uranium.
How does it generate large amounts of energy?
When an atom of uranium-238 is bombarded with slow-moving neutrons it splits the nuclei into two smaller atoms and three fast neutrons, which go on to split more atoms, this forms a chain reaction.
This process is called nuclear fission and releases a huge amount of energy very quickly.
In a nuclear reactor, a controlled chain reaction takes place and thermal energy is released which is used to make steam to turn the turbines which then turn generators that generate electricity.
Nuclear energy is much more efficient than fossil fuel energy because a very small amount of uranium (about 1kg) can generate as much electricity as 55 tonnes of coal.
Other alternative to fossil fuels are:
- Wind power
- Hydroelectric power
- Solar energy
- Geothermal energy
- Biofuels
Please comment below if you have any questions or spot any errors I may have made :)